Friday, March 4, 2011
Thursday, March 3, 2011
Tuesday, February 22, 2011
Thursday, February 3, 2011
Basic electronics
CONDUCTOR : Materials in which electron can move freely at room temperature are called conductor
e.g. Copper,Aluminium,Iron etc
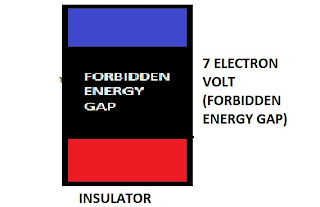
BLUE PART: CONDUCTION BAND
RED PART: VALANCE BAND
BLACK PART: FORBIDDEN ENERGY GAP
INSULATOR : Materials in which electrons can not move freely at room temperature are called insulator
e.g. Wood,Plastic etc
SEMICONDUCTOR :Materials which act as insulator at room temperature but act as conductor in specific condition (environment) called semiconductors
e.g. Germanium,Silicon etc
P-Type material :When trivalent impurity is added to pure semiconductor material,then it will create one hole in the valance band,this material is called as p-type material
N-Type material :When pentavalent impurity is added to pure semiconductor device then it will create one electron in the valence band, this material is called as n-type material
Doping : The process by which impurity is added to pure semiconductor material is called as doping
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)